Variation, Mutation and Recombination
Variation, Mutation and Recombination: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Recombination of Genes, Mutation, Gene Mutations, Importance of Variation in Organisms, Continuous Variation, Discontinuous Variation, Silent Mutation, Polyploidy, Deletion in Chromosomal Structure, etc.
Important Questions on Variation, Mutation and Recombination
Given below is a representation of a kind of chromosomal mutation. What is the kind of mutation represented?
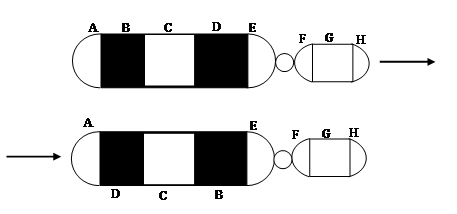
Define tetraploidy.
The phenomenon of having an extrachromosome segment attached to its normal homologous chromosome is called
What is duplication in chromosome structure?
The loss of an intercalary segment of a chromosome is called inversion.
Write a note on the deletion in the chromosomal structure.
Define continuous variation.
Turner syndrome is a case of trisomy.
Which of the following is a case of tetrasomy?
Down's syndrome is a case of
Define the term hyperploidy.
What is the effect of nullisomy in humans?
Nullisomy is caused due to _____ during meiosis.
Briefly explain nullisomy with an example.
Monosomy is a type of aneuploidy.
Define hypoploidy with an example in human.
Mention one utility of silent mutation in research.
Justify the statement: Silent mutations are evolutionarily neutral.
A nucleotide change in the DNA that result in an amino acid change in the protein is “silent” mutation.
What is effect of silent mutation?
